Transgenic Animals Definition Biology

Toxicity testing in such animals will allow us to obtain results in less time.
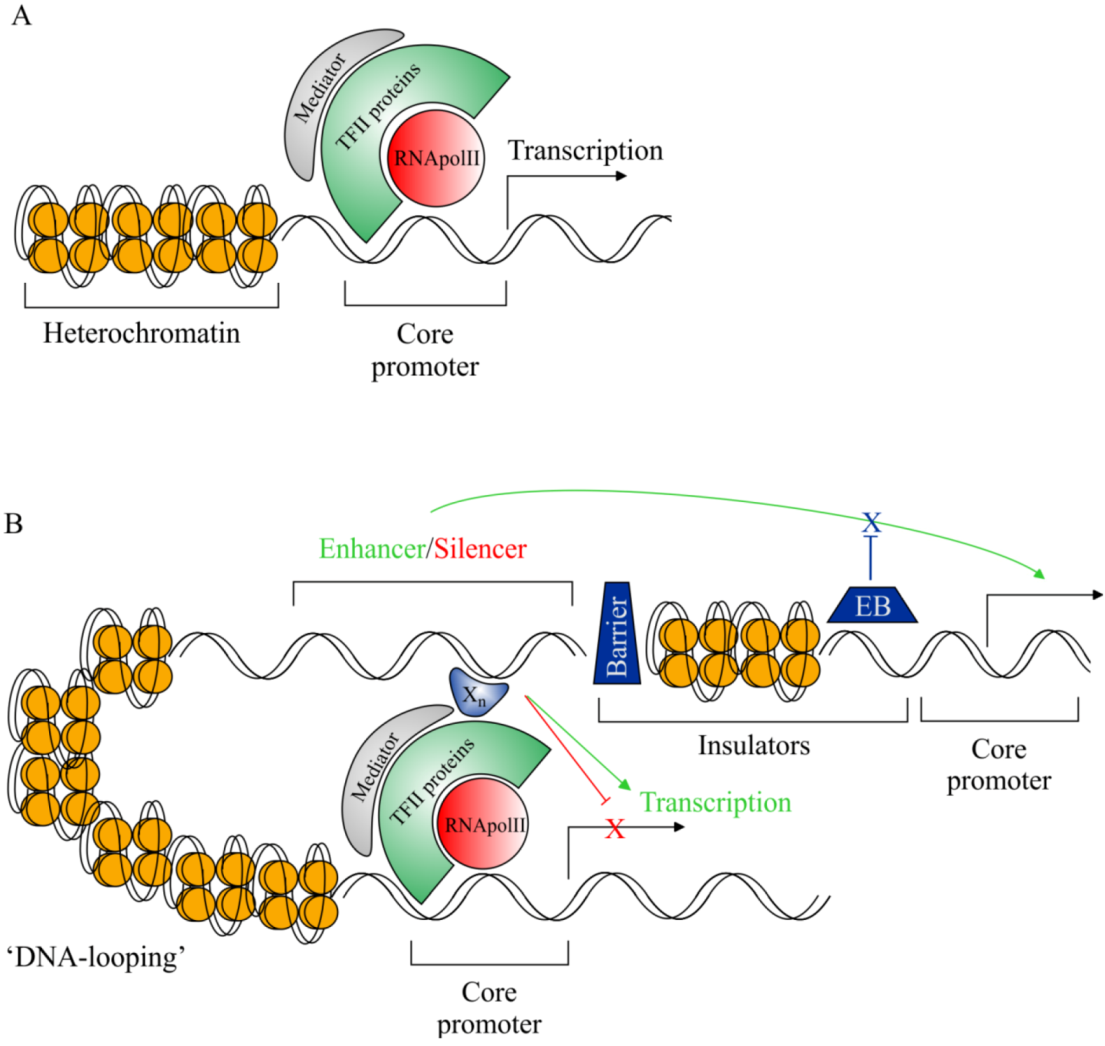
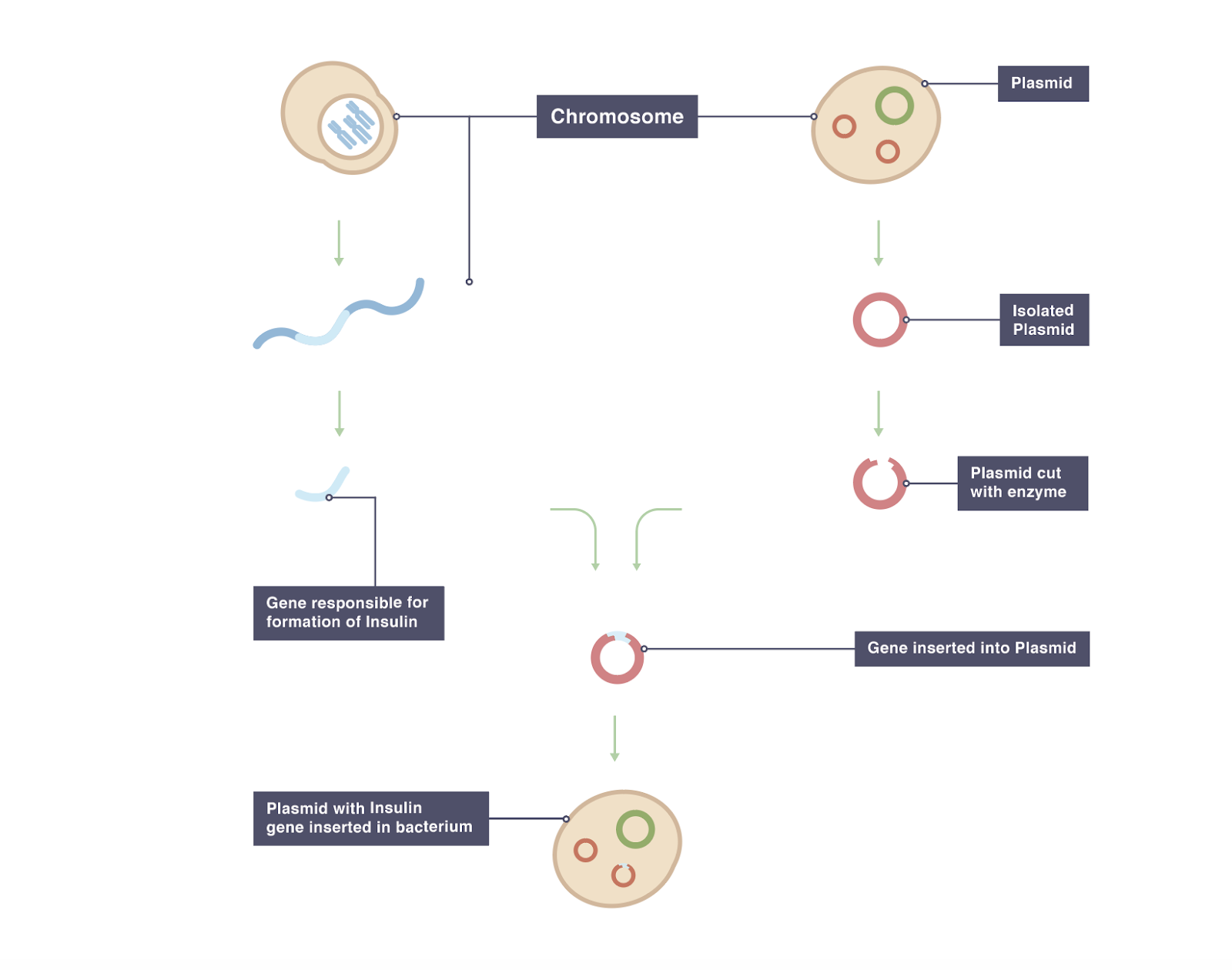
Transgenic animals definition biology. A transgenic animal is one that carries a foreign gene that has been deliberately inserted into its genome. Transgenic animal genetically engineered animalor offspring of genetically engineeredanimals. The foreign gene is constructed using recombinant DNA methodology.
BTransgenic animals are made that carry genes which make them more sensitive to toxic substances than non-transgenic animals. Transgenic animal industrial applications 3 chemical safety testing toxicity-sensitive transgenic animals animal bioreactor protein production. The term transgenic animal refers to an animal in which there has been a deliberate modification of the genome - the material responsible for inherited characteristics - in contrast to spontaneous mutation FELASA September 1992 revised February 1995.
By DAMARIS BENNY DANIEL II Msc. They may also be engineered to have advantageous or useful traits. Moreover in order to devise a cure for these diseases the transgenic animals are used as model organisms.
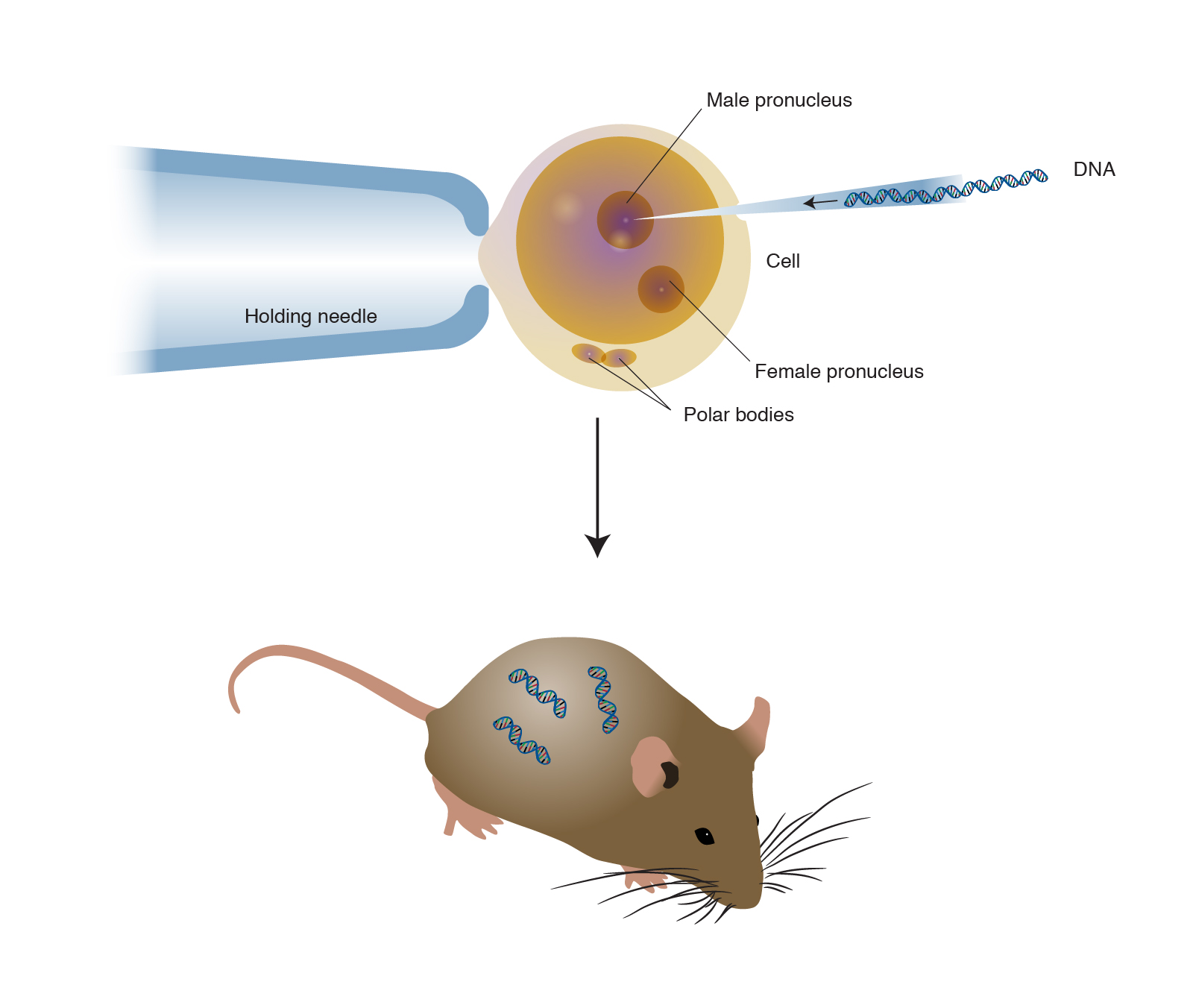
The foreign DNA or transgene that is transferred to the recipient can be from other individuals of the same species or even from unrelated species. Animals usually are made transgenic by having a small sequence of foreign DNA injected into a fertilized egg or developing embryo. The first successful transgenic animal was a mouse6 A few.
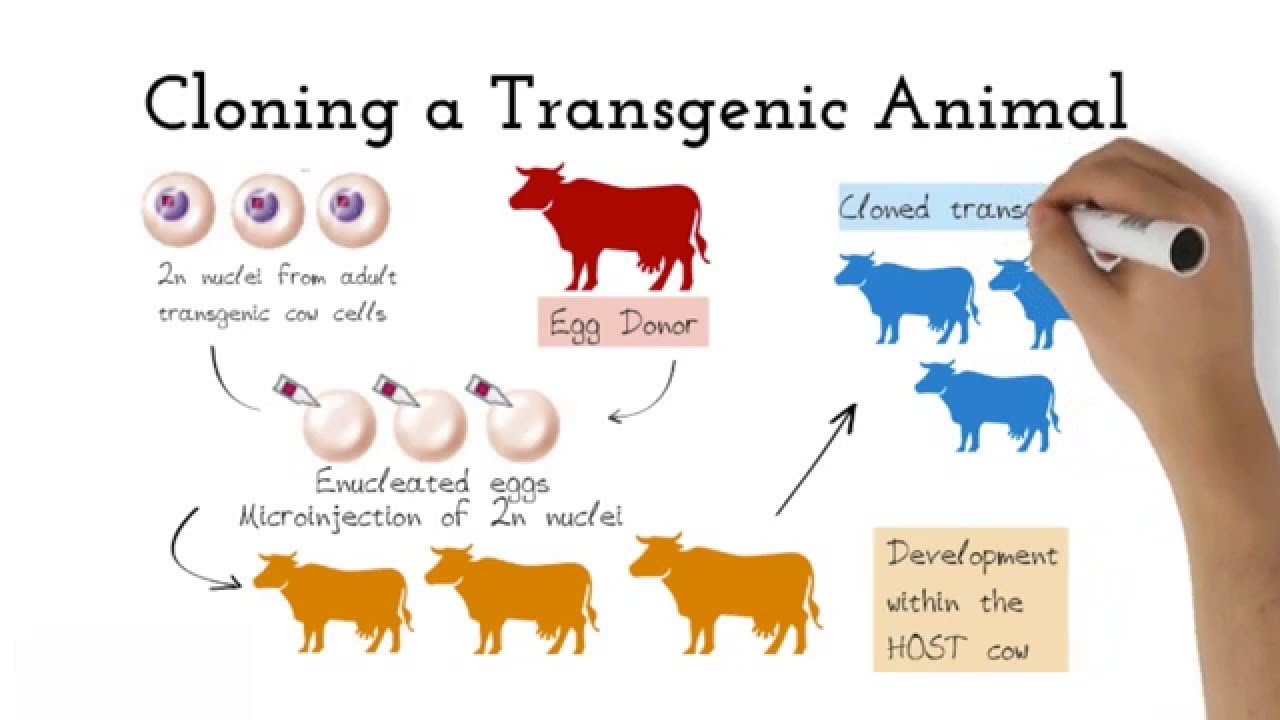
A transgenic animal is one whose genome has been altered by the transfer of a gene or genes from another species or breed. Animals transgenic animals or the offspring of such animals into which cloned genetic material has been experimentally transferred by microinjection of foreign dna either directly or into embryos or differentiated cell types. Arise from pluripotent stem cells.
Full article A transgenic animal is one whose genome has been changed to carry genes from other species. Transgenic animals have also been produced to study animal biochemical processes and human diseases or used to produce pharmaceuticals and other proteins. Theoretically all living beings can be genetically manipulated.

_1602913203_391831-5.jpg)