Food Chain Definition Biology

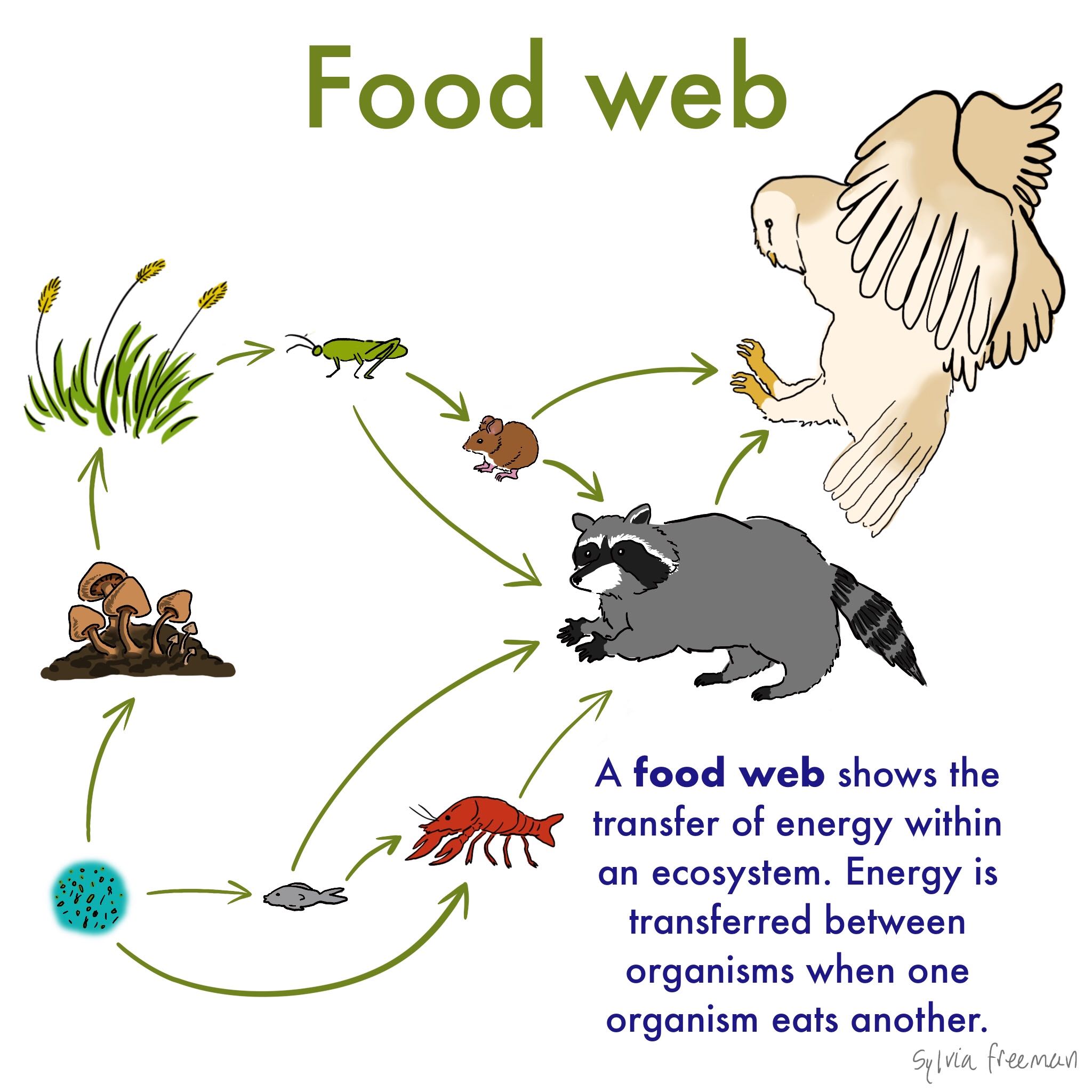
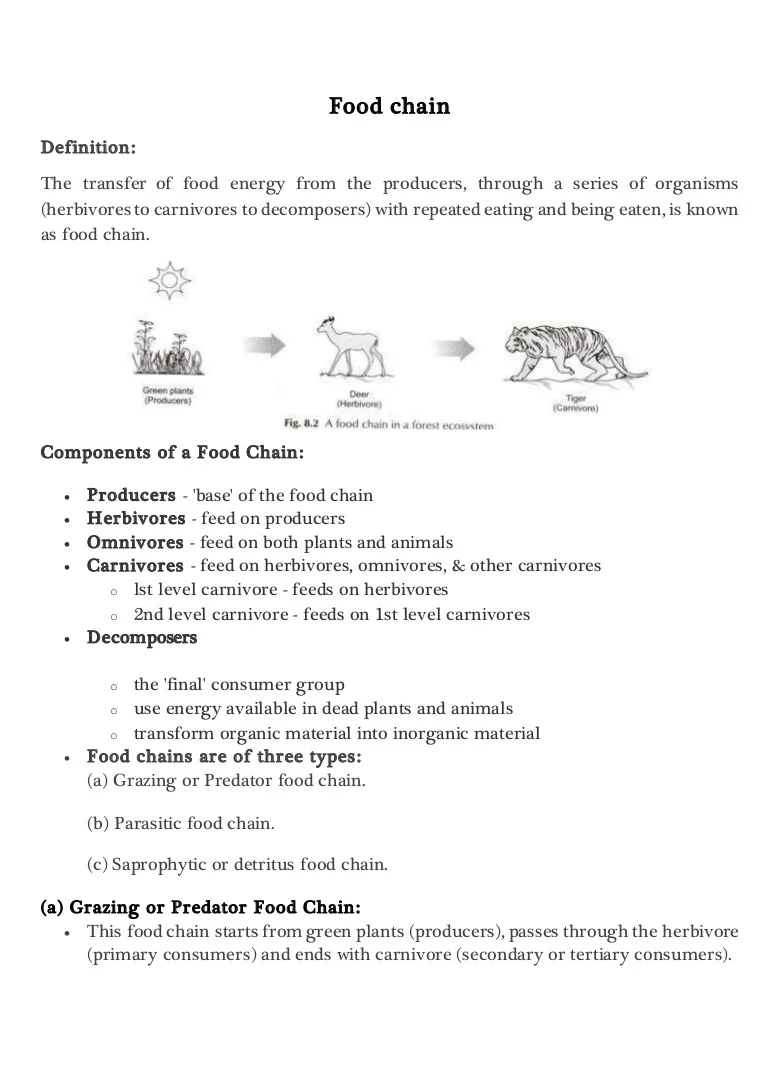
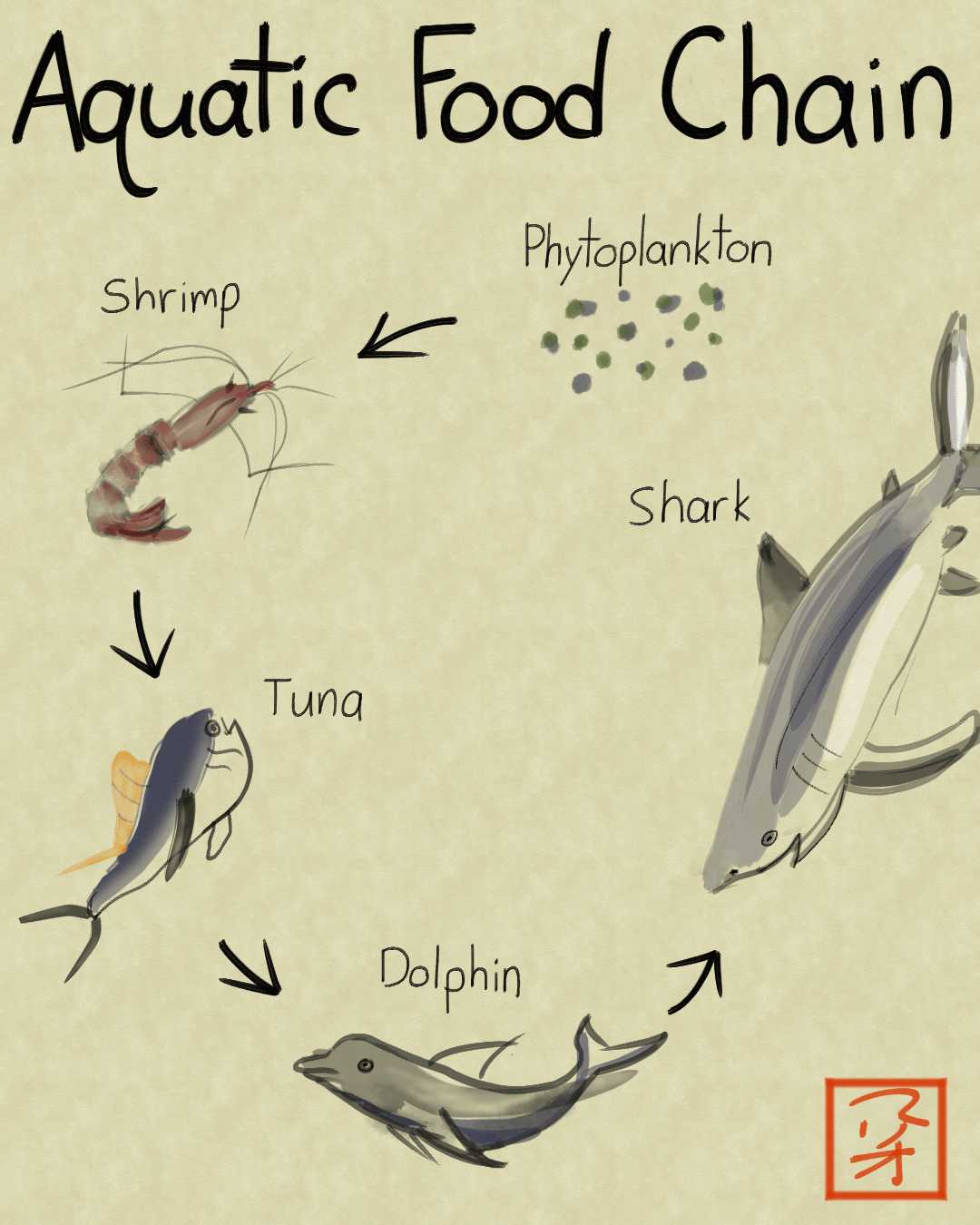
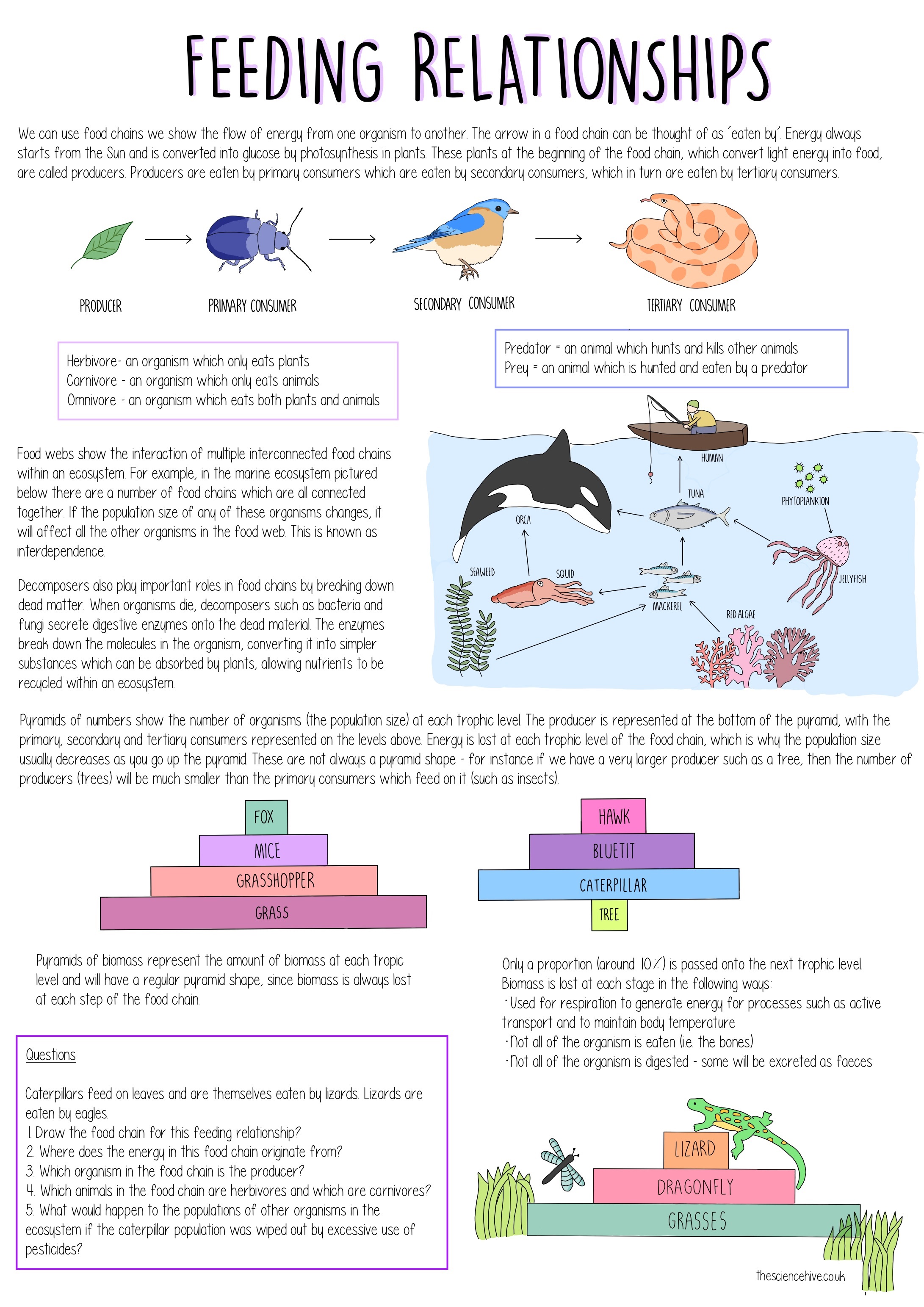
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web starting from producer organisms such as grass or trees which use radiation from the sun to make their food and ending at apex predator species like grizzly bears or killer whales detritivores like earthworms or woodlice or decomposer species such as fungi or bacteria.
Food chain definition biology. 5 hours ago A food chain is a series of interdependent relationships between living organisms. A series of living things that are connected because each group of things eats the group below. This occurs when one organism consumes another organism.
It shows the flow of energy and materials from one organism to the next beginning with a producer. What are food chains. A community of animals plants and microorganisms together with the habitat where they live.
In ecology a food chain is a series of organisms that eat one another so that energy and nutrients flow from one to the next. Food Chain Definition Biology Idalias Salon. The trophic chain food chain or food chain is known as the mechanism by which organic matter nutrients and energy are transferred by the different types of living things that make up a biological community or ecosystem.
The producers are represented primarily by the green plants and to a lesser extent by the photosynthetic bacteria. A food chain is the linear not branched sequence in which a living organism serves as food for another starting with the producers and going up to the decomposers. It is the process by which nutrients are transferred between the different species that make up a biological community.
The organisms that feed on dead organic matter or detritus are known as detritivores or decomposers. Food chain - ecology a community of organisms where each member is eaten in turn by another member. Energy is not created or destroyed.
See more Encyclopedia articles on. Use words in a sentence. Its name comes from the Greek trophies to feed to nourish.