Cellular Respiration In Plants Equation

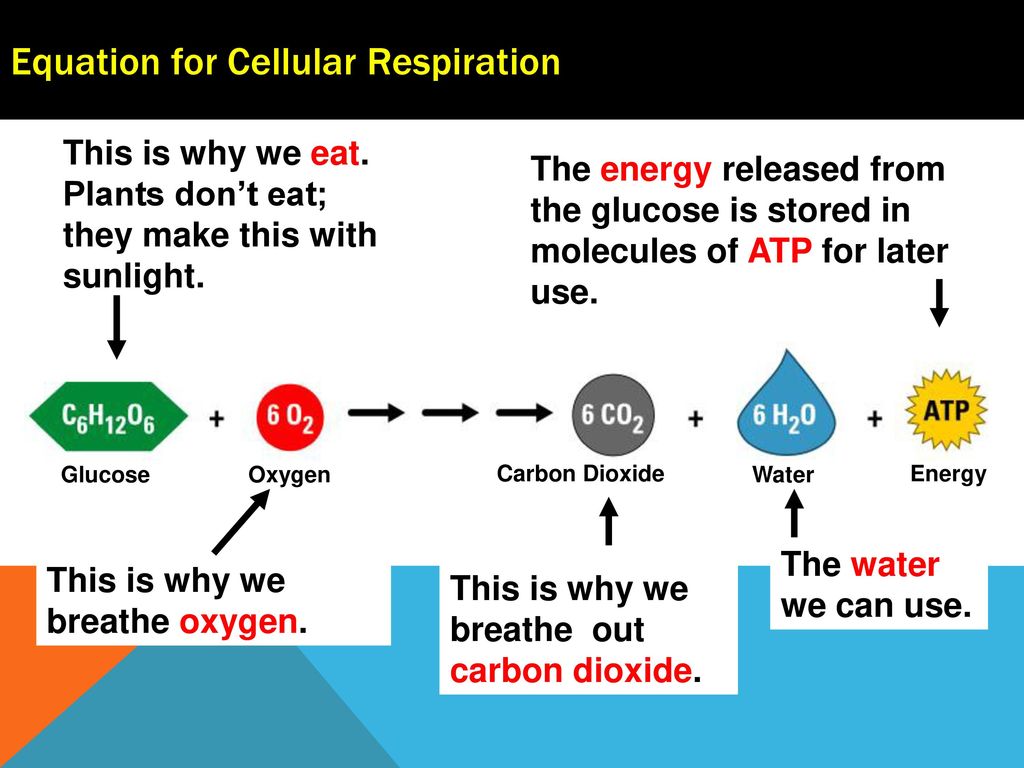
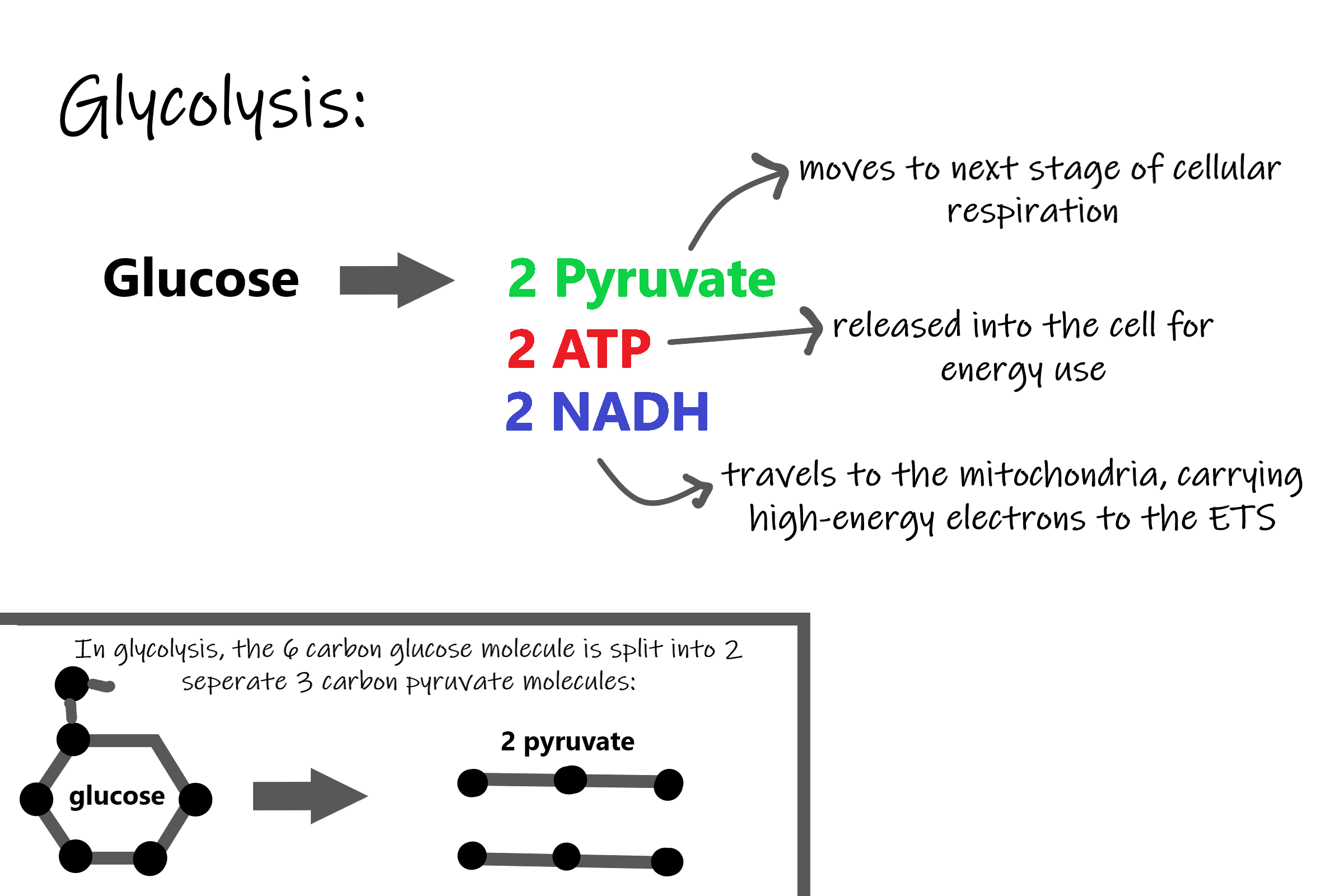
L Glucose 4ADP 4Pi 2NAD 2Pyruvic acid 4ATP 2NADH l Two molecules of ATP were used up in the initial steps of glycolysis.
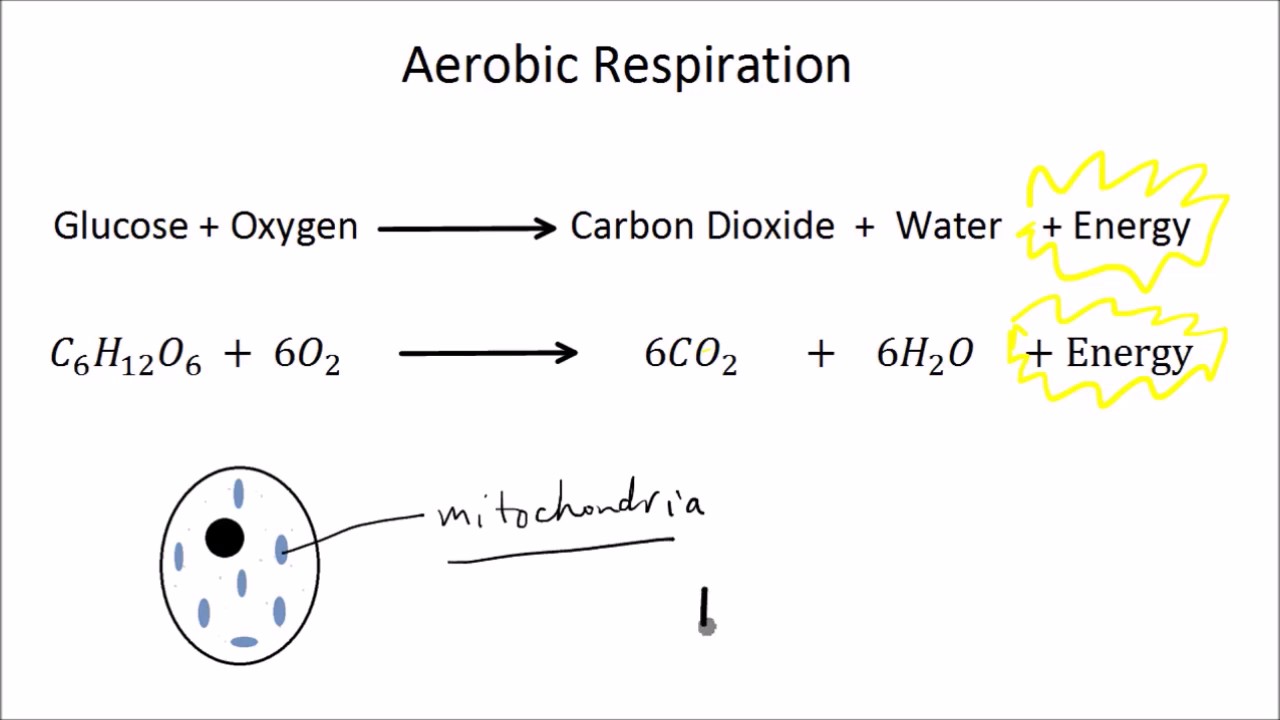
Cellular respiration in plants equation. Name the respiratory organ in woody stems. Thus the net gain of ATP during glycolysis is 4 2 2 ATP. C 6 H 12 O 6 glucose 6O 2 36 ADP depleted ATP 36 P i phosphate groups 6CO 2 6H 2 O 36 ATP.
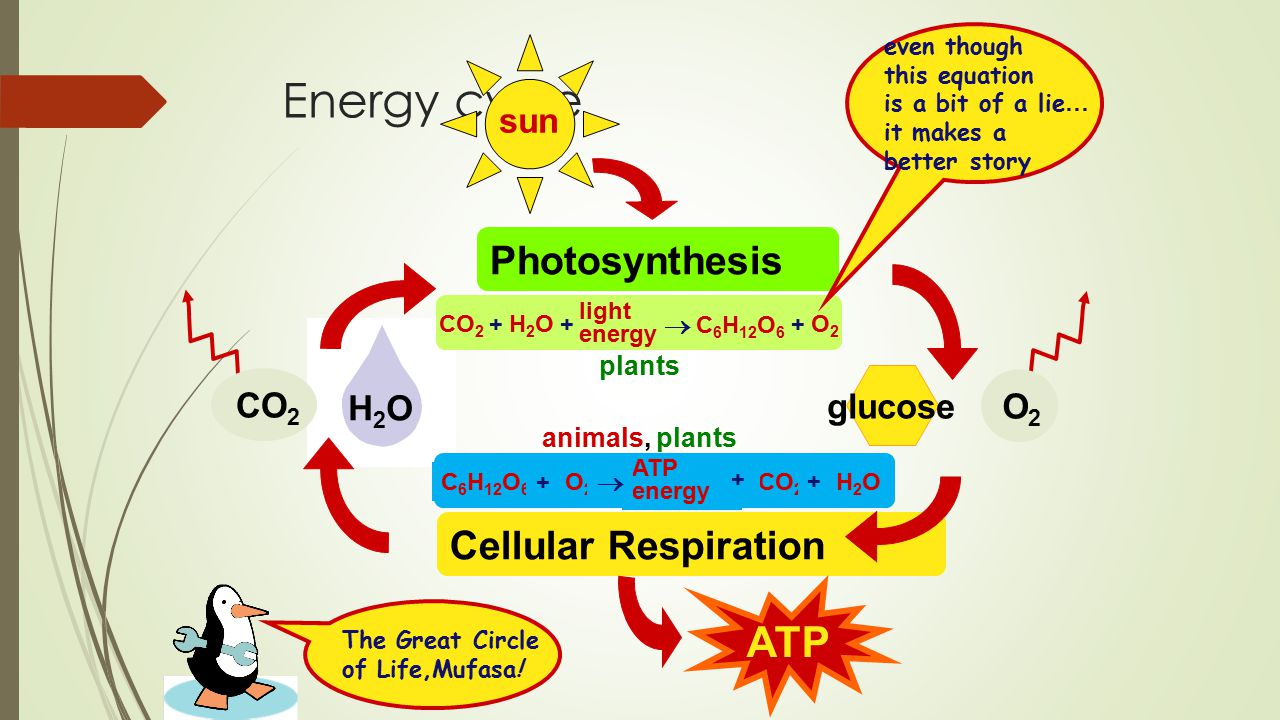
Understanding Cellular Respiration Here are three visual depictions of cellular respiration an equation an output description and an illustration. Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as. Photosynthesis Is An Anabolic Process Whereas.
Also 2NADH H are produced. Glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 Oxygen O 2. Cellular respiration has the same chemical equation as photosynthesis.
6o2 c6h12o6 à 6co2 6h2o energy the energy that is released by cellular respiration is in the form of. This process yields a lot of ATP for the plant to use for growth and reproduction. It is the process in which the oxidation of glucose takes place in the absence of.
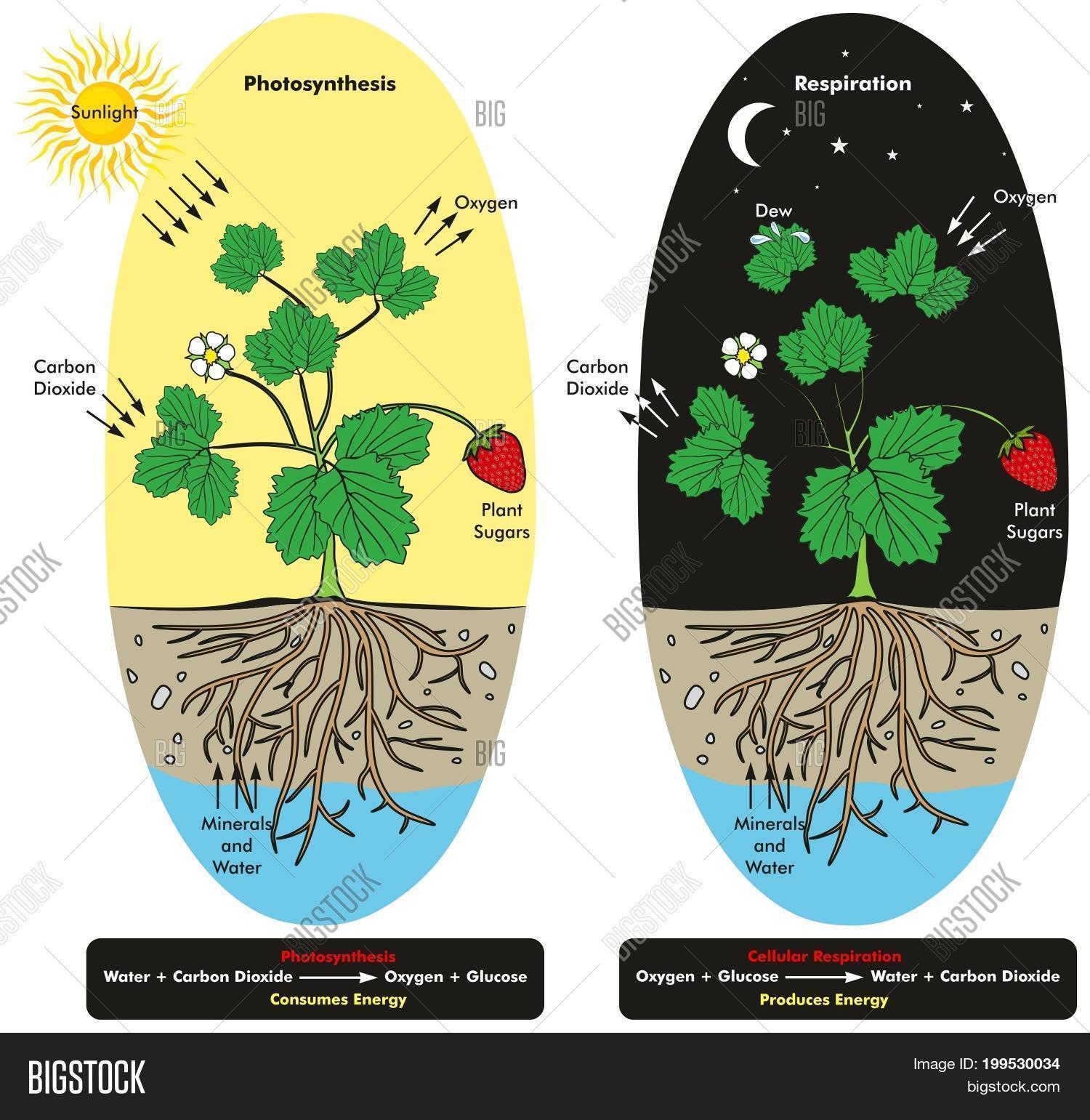
The word equation for cellular respiration is glucose sugar oxygen carbon dioxide water energy as atp. Cellular respiration or aerobic respiration is a series of chemical reactions which begin with the reactants of sugar in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water as waste products. The chemical equation of cellular respiration is expressed as oxygen glucose - carbon dioxide water heat energy.
The glucose is then used by the plants or organisms that consume the plants for the process of cellular respiration to make atp. It is an exergonic reaction where high-energy glucose molecules are broken down into carbon dioxide and water. It is also known as a catabolic reaction as a large molecule like a carbohydrate is broken down into smaller molecules.