Cell Membrane Structure Journal

Introduction The cell membrane is a biological membrane that separates the intracellular environment from.
Cell membrane structure journal. The cell membrane is a complex barrier separating every cell from its external environment. In particular we welcome work that uses modern experimental or computational methods including but not limited to those with microscopy diffraction NMR computer simulations or biochemistry aimed at membrane associated or membrane embedded proteins or model membrane. For the same token a bacterial toxin does not insert into the membrane through a nonlamellar phase nor two membranes fuse via a rhombohedral phase.
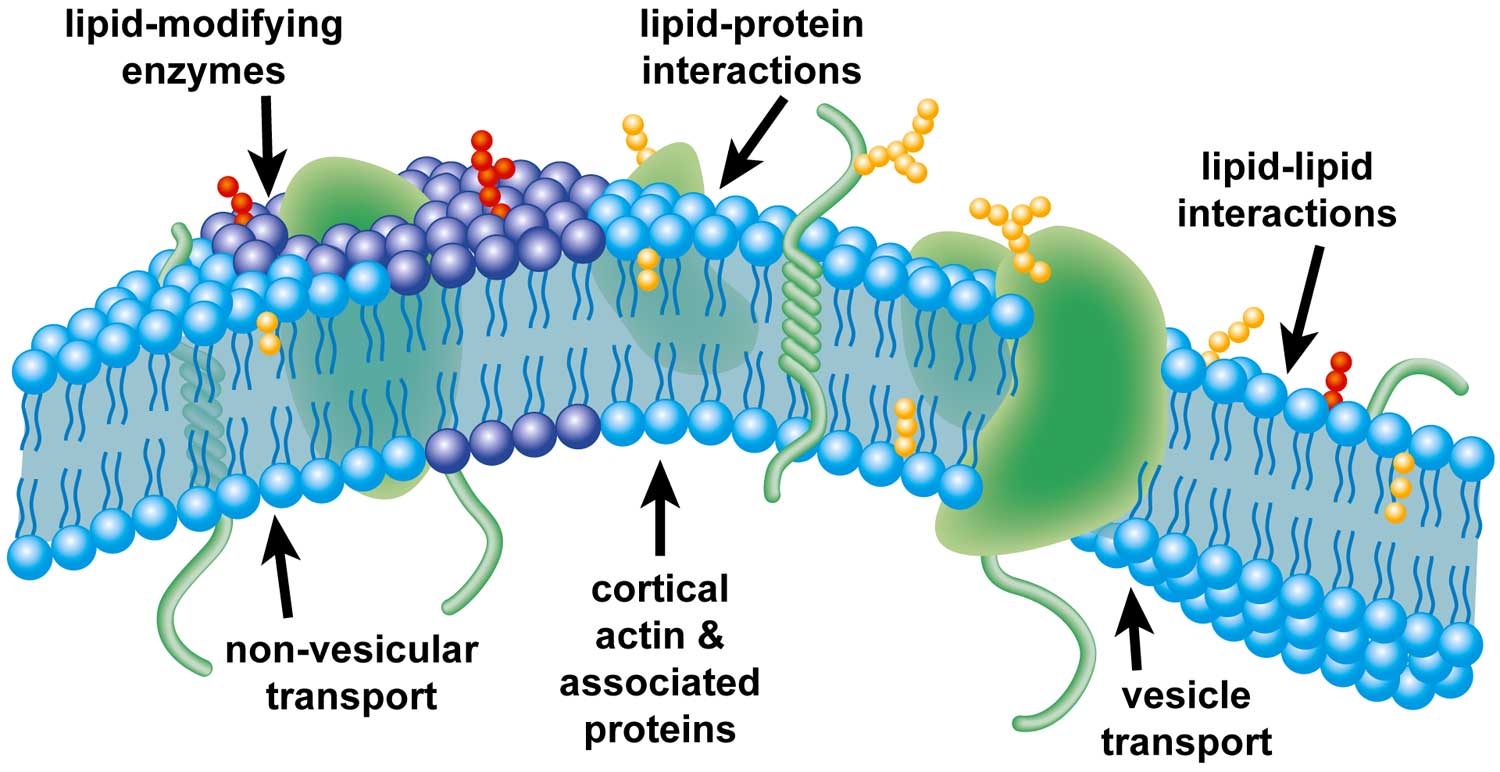
In plant cells the membrane encapsulates the protoplasm. Recent studies of structure-function relationships in biological membranes have revealed fundamental concepts concerning the regulation of cellular membrane function by membrane lipids. The fascination of membrane research is that the functionality of the cell membrane is dependent on the carefully orchestrated and mutually interdependent properties of lipids and proteins.
This organelle is also referred to as plasma membrane. J D Robertson. Blood group active components of the human red cell membrane.
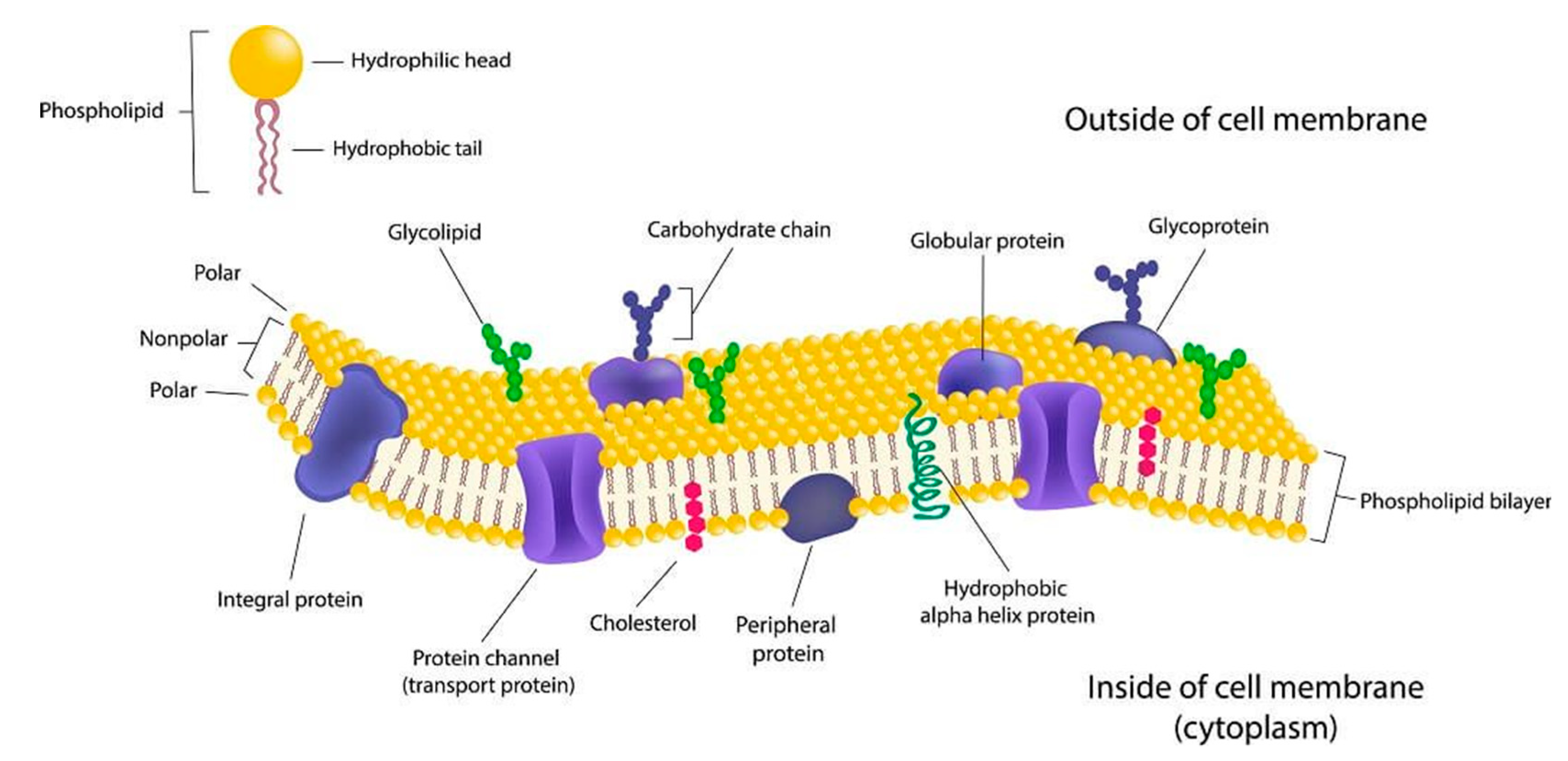
The cell membrane is a fluid mosaic of proteins floating in a phospholipid bilayer. This Selectively Permeable membrane regulates what passes into and out of the cell. The cell membrane is one of the most complicated biological complexes and long-term fierce debates regarding the cell membrane persist because of technical hurdles.
Alexa Fluor Dye Conjugates. Ad Reveal the Subcellular Localization in Cell Imaging Applications. The work described here addresses questions from a broad range of areas including cell adhesion membrane trafficking and activation of cells.
THE formation of single stable bimolecular lipid and proteolipid1 membranes up to 10 mm2 in area has been accomplished routinely in 01 M saline solution by methods analogous to the formation of. L Thefluid mosaicmodelofthestructure of cell membranes Science 175 18. Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out.