Cell Membrane Structure And Function A Level

The membrane is examined in detail later.
Cell membrane structure and function a level. This structure can even be called the inner membrane to distinguish it from the outer membrane present in gram-negative bacteria. The separation of different parts of the cell with different functions by using membranes is called compartmentalisation providing distinct conditions for different processes. The fundamental structure of the plasma membrane.
Membrane Structure and Function Plasma Membrane. Act as a barrier to most water-soluble substances the non-polar fatty acid tails prevent polar molecules or ions from passing across the membrane. Organisms are composed of cells and these cells have specific structures within in them that allow them to carry out their functions.
The membrane also contains membrane proteins including integral proteins that go across the membrane serving as membrane. Cell Membrane or Plasma Membrane. For eg the skin is made up of a large number of cells.
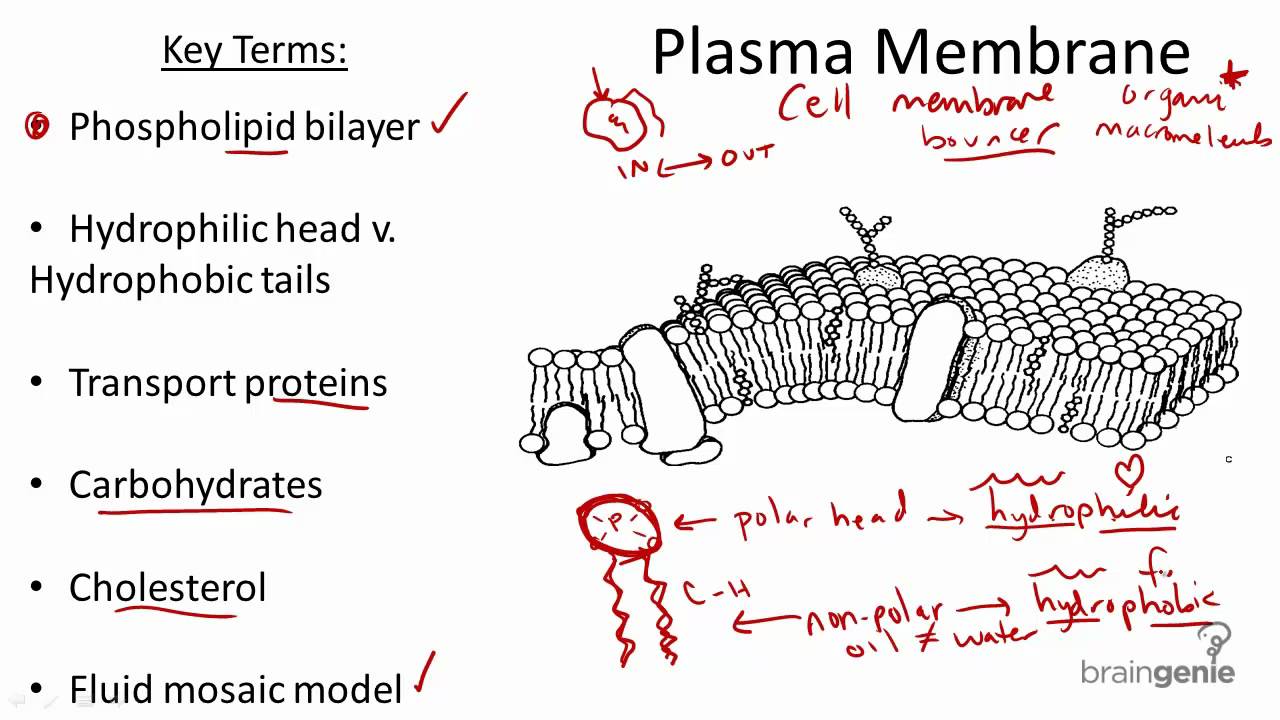
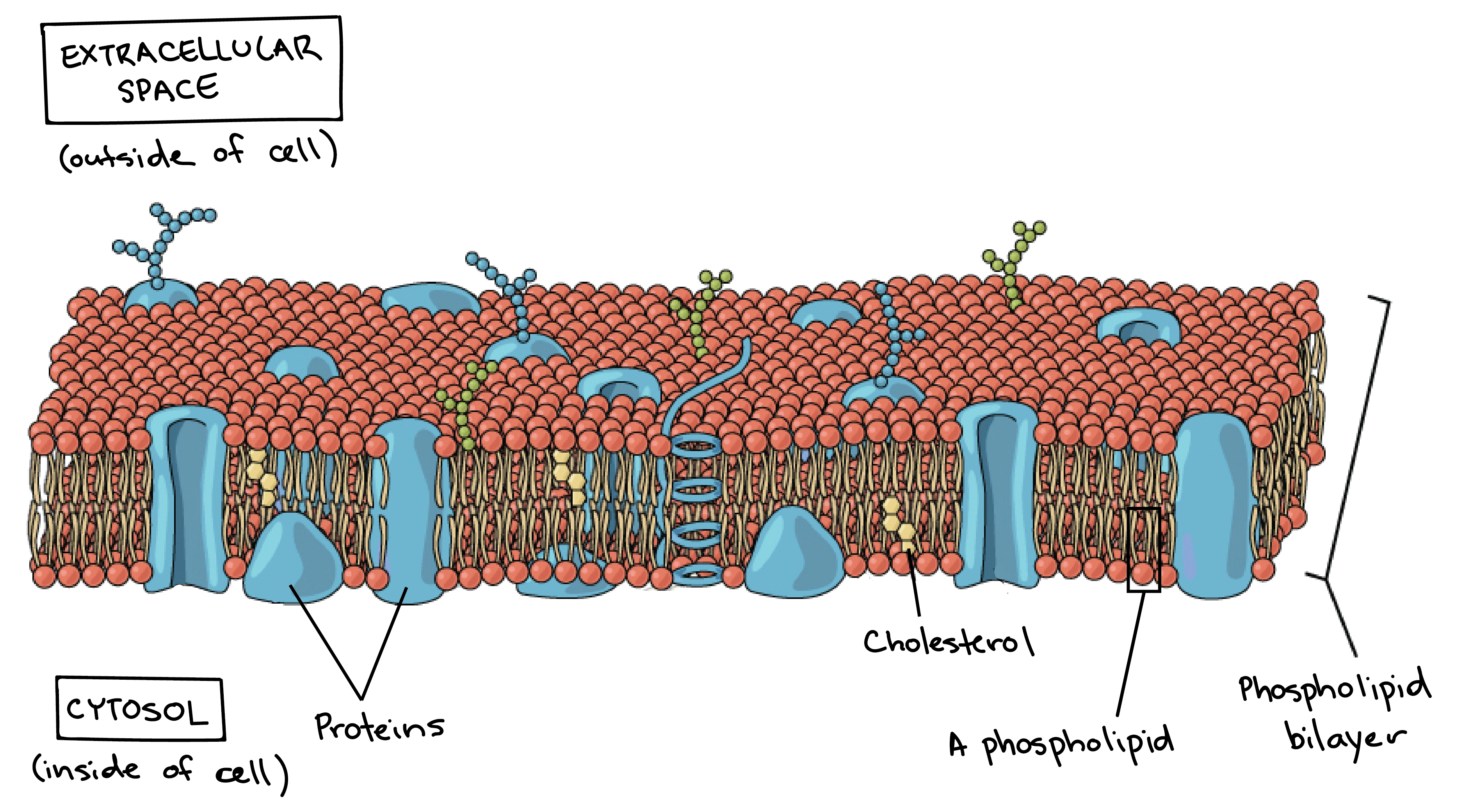
It is a fluid mosaic of lipids proteins and carbohydrate. Different organelles have distinct structures and functions. Proteins and lipids are the major components of the cell membrane.
This is a thin flexible layer round the outside of all cells made of phospholipids and proteins. Form the basic structure of the membrane phospholipid bilayer The tails form a hydrophobic core comprising the innermost part of both the outer and inner layer of the membrane. Both the cell surface membrane and the membranes surrounding certain organelles have the same basic structure.
The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer including cholesterols that sit between phospholipids to maintain their fluidity at various temperatures. Membranes formed from phospholipid bilayers help to compartmentalise different regions within the cell as well as forming the cell surface membrane Exam Tip An example of a membrane-bound organelle is the lysosome found in animal cells each containing many hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many different kinds of biomolecule. The cell wall and the cell membrane are the main components that function to provide support and structure to the organism.