Animals In The Desert Food Chain

Your browser does not support the audio element.
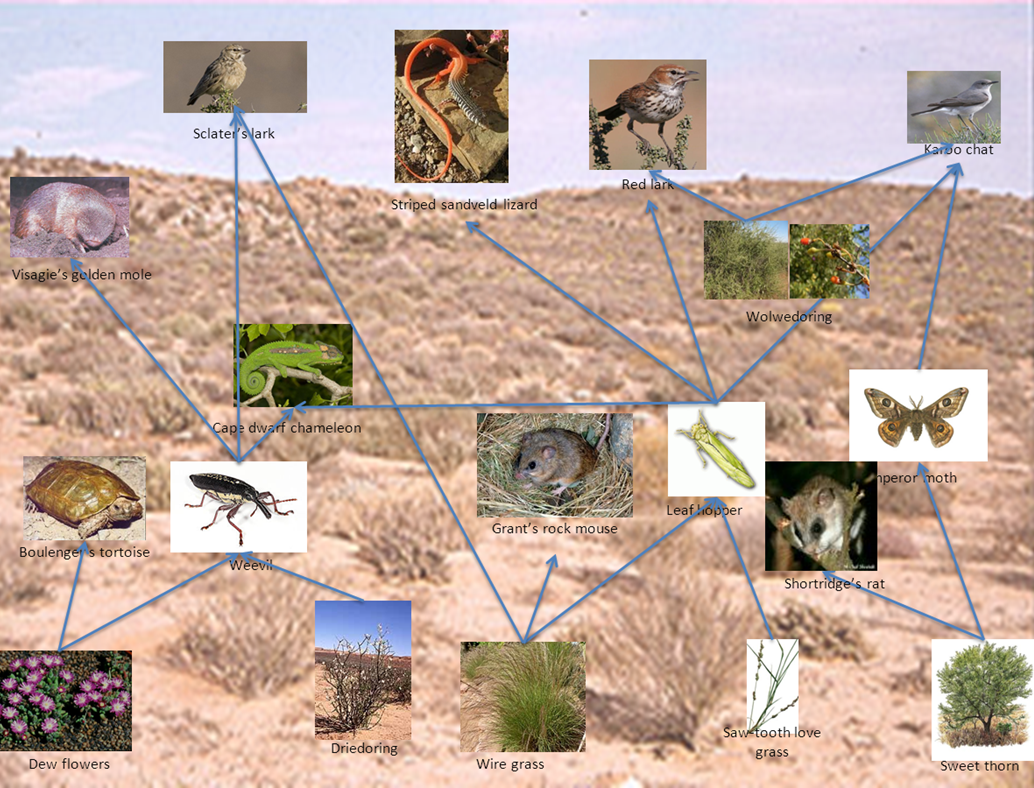
Animals in the desert food chain. They learn the difference between producers and consumers and study how these organisms function within their communities as participants in various food chains. If a hawk eats the frog it becomes prey. Detritivores are organisms that eat nonliving plant and animal remains.
In the Mojave the desert kit fox is one of the secondary consumers that feeds on cottontail. These animals are fewer in numbers than the herbivores as one secondary consumer consumes many herbivores for survival. A frog is a predator when it eats an insect.
Another example would be of the horned lizard that feeds on herbivores and takes place of the secondary consumer in the food chain. Insects Lizards Apache Pocket Mouse Kangaroo Rat Desert Cottontail Jackrabbit. Some are called scavengers as they feed on dead animalsFinally there are decomposers like desert mushrooms and bacteria and worms which decompose the dead animals.
The herbivores are mostly small animals like rodent kangaroos rats and lizards. Of course the animals herbivores carnivores or omnivores depend totally on the plants the foundation of the food chain for survival. The coyotes natural predator was at one time the wolf.
It eats nuts and berries plants It also eats fish animals. As you can see there are many species of animals in the desert that eat each other. Detritivores and decomposers are the final part of food chains.
Man is the top predator in any desert environment whether by intention or accident. Food Chains and Food Webs - Balance within Natural Systems. So a desert food chain starts with a saguaro cacti followed by a wood rat then a diamondback rattlesnake and finally a red-tailed hawk.